Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DME4RA8)
| Drug Name |
Amodiaquine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Amodiachin; Amodiachinum; Amodiaquin; Amodiaquina; Amodiaquinum; Basoquin; CQA; Camochin; Camoquin; Camoquinal; Camoquine; Flavoquin; Flavoquine; Miaquin; Sunoquine; Amodiaquine hydrochloride; Amodiaquine USP24; SN 10751; AMODIAQUINE, FLAVOQUINE; Amodiaquina [INN-Spanish]; Amodiaquinum [INN-Latin]; CAM-AQ 1; CAM-AQI; Cam-AQ1; Camoquin (TN); Flavoquine (TN); SN 10,751; WR-002977; Amodiaquine (USAN/INN); Amodiaquine [USAN:INN:BAN]; Amodiaquine, ring-closed; S. N. 10751
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antimalarials
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Plasmodium
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
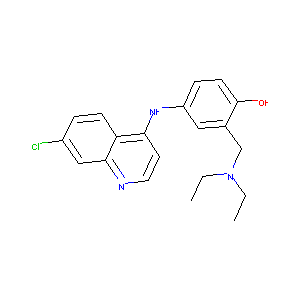 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 355.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
